Accurate and robust logical driving behavior based on V2I communication for Connected & Autonomous Transport (CAT) at XL business park
Carla is a software program designed for researching autonomous driving that is available for free use and modification. Its interface is robust and enables the development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. On the other hand, MATLAB, which is widely utilized, particularly by engineers, requires no introduction. Its numerous features facilitate rapid product development. Therefore, in this work a combination of these two software was used to create V2I application.
Software Requirements:
• Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS.
• CARLA Simulator: The CARLA 0.9.13 version of the simulator was used in this project. This version of the simulator provides a stable and reliable environment for simulating autonomous driving scenarios.
• Python: Python 3.8.10 was used as the programming language for the CARLA simulator. This version of Python provides a robust and flexible environment for developing and testing autonomous driving algorithms.
• Unreal Engine: Unreal Engine 4.26.2 was used as the game engine for the CARLA simulator. This version of the engine provides high-quality graphics and physics simulation capabilities for creating realistic autonomous driving scenarios.
• Roadrunner 2022b was used to create road network
• MATLAB 2020b
Hardware Requirements:
• Processor: Intel® Core™ i7-11800H (2.4 GHz base clock, up to 5.0 GHz max turbo frequency, 8 cores, 16 threads)
• Graphics Card: NVIDIA® GeForce® RTX 3070 (8 GB GDDR6 memory)
• Memory: 32 GB DDR4-3200 SDRAM (2 x 16 GB)
• Storage: 1 TB PCIe® NVMe™ M.2 SSD
CARLA requires many different kinds of software to run. Some are built during the CARLA build process itself, such as Boost.Python. Others are binaries that should be installed before starting the build (cmake, clang, different versions of Python, etc.). To install these requirements, run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update &&
sudo apt-get install wget software-properties-common &&
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-toolchain-r/test &&
wget -O - https://apt.llvm.org/llvm-snapshot.gpg.key|sudo apt-key add - &&
sudo apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.llvm.org/xenial/ llvm-toolchain-xenial-8 main" &&
sudo apt-get update
To avoid compatibility issues between Unreal Engine and the CARLA dependencies, use the same compiler version and C++ runtime library to compile everything. The CARLA team uses clang-8 (or clang-10 in Ubuntu 20.04) and LLVM's libc++. Change the default clang version to compile Unreal Engine and the CARLA dependencies.
sudo apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.llvm.org/focal/ llvm-toolchain-focal main"
sudo apt-get install build-essential clang-10 lld-10 g++-7 cmake ninja-build libvulkan1 python python-dev python3-dev python3-pip libpng-dev libtiff5-dev libjpeg-dev tzdata sed curl unzip autoconf libtool rsync libxml2-dev git
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/clang++ clang++ /usr/lib/llvm-10/bin/clang++ 180 &&
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/clang clang /usr/lib/llvm-10/bin/clang 180
Starting with CARLA 0.9.12, users have the option to install the CARLA Python API using pip or pip3. Version 20.3 or higher is required. To check if you have a suitable version, run the following command:
pip3 -V
If you need to upgrade:
pip3 install --upgrade pip
You must install the following Python dependencies:
pip install --user setuptools &&
pip3 install --user -Iv setuptools==47.3.1 &&
pip install --user distro &&
pip3 install --user distro &&
pip install --user wheel &&
pip3 install --user wheel auditwheel
Starting with version 0.9.12, CARLA uses a modified fork of Unreal Engine 4.26. This fork contains patches specific to CARLA.
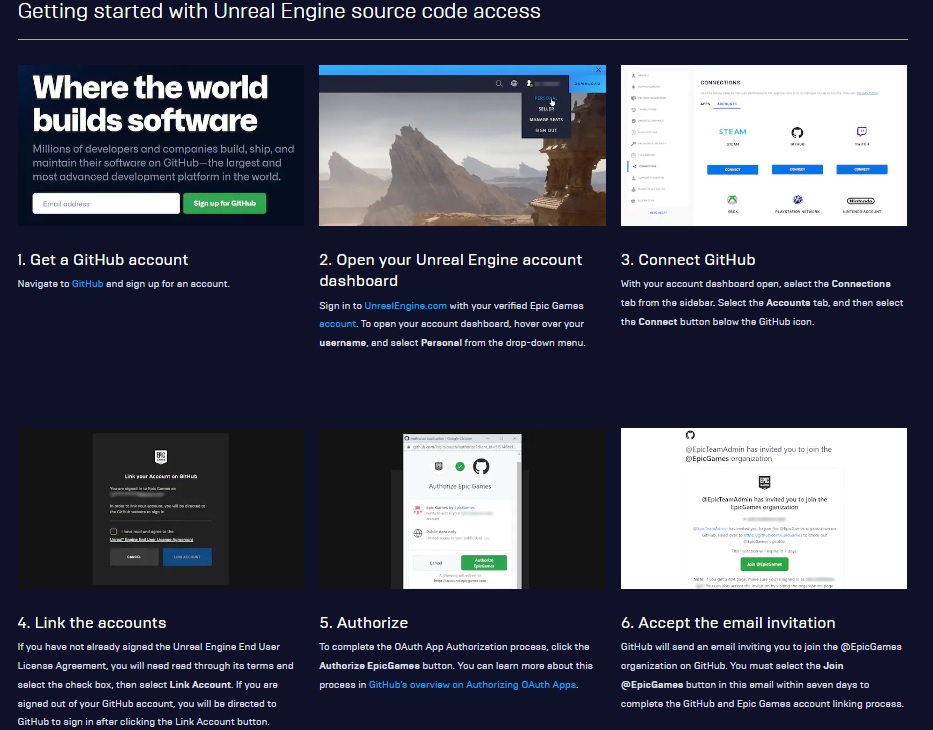
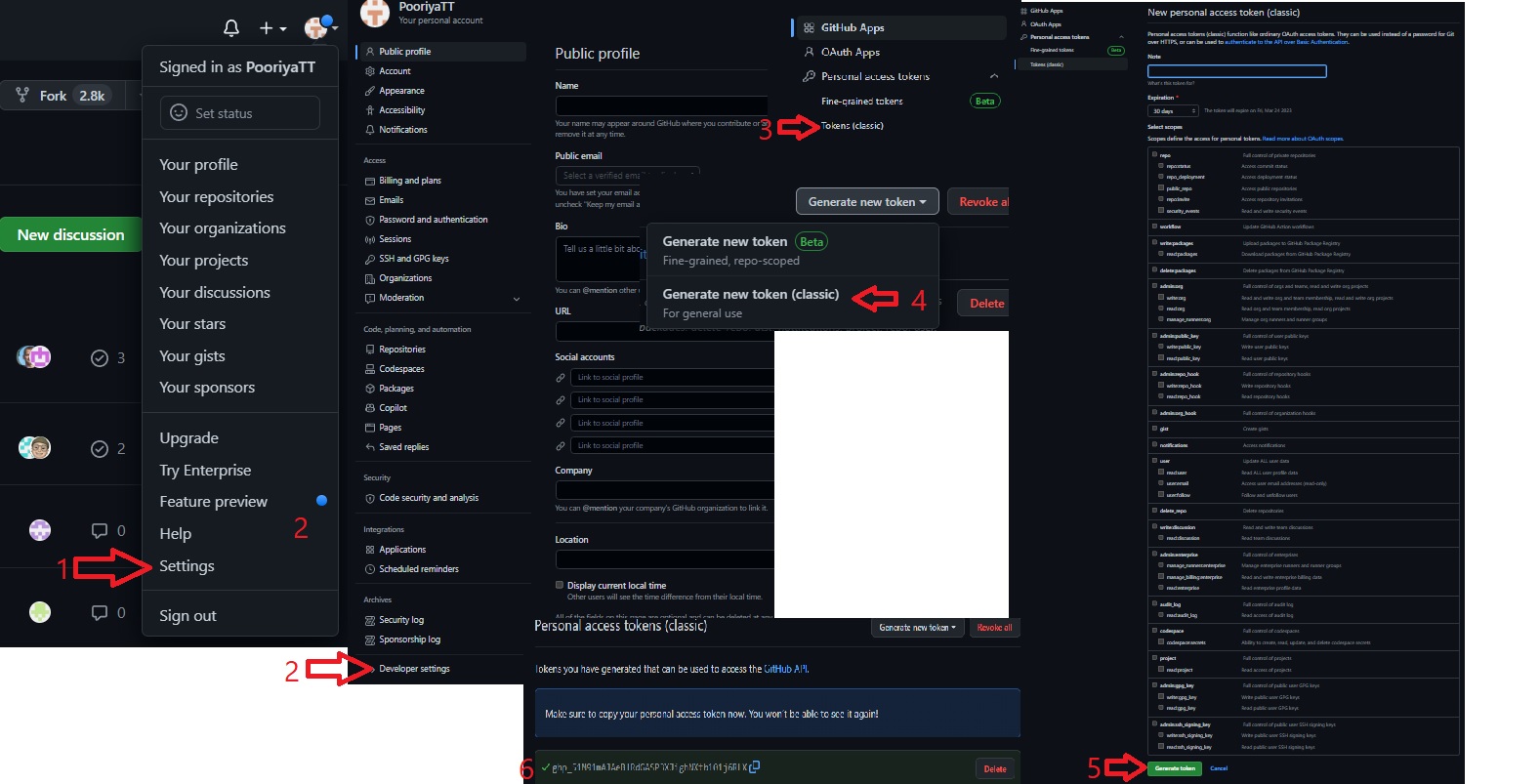
Be aware that to download this fork of Unreal Engine, you need to have a GitHub account linked to Unreal Engine's account. If you don't have this set up, please follow the following steps.
When you follow the steps as mentioned above you need to get a personal token for cloning the Unreal engine which will be your password requested in the terminal during executing the following code which is the first step of installing unreal engine.
- Clone the content for CARLA's fork of Unreal Engine 4.26 to your local computer:
git clone --depth 1 -b carla https://github.com/CarlaUnreal/UnrealEngine.git ~/UnrealEngine_4.26
At this stage you are propmpet to use your username and password (your user name is your email which you use for Github and Unreal engine during the previous steps and for Password following steps are required)
after clicking on generating the token you will se a code which will be your persoanl token and it should be coppied and pasted to the terminal to start cloning the unreal engine.
- Navigate into the directory where you cloned the repository:
cd ~/UnrealEngine_4.26
- Make the build. This may take an hour or two depending on your system.
./Setup.sh && ./GenerateProjectFiles.sh && make
- Open the Editor to check that Unreal Engine has been installed properly.
cd ~/UnrealEngine_4.26/Engine/Binaries/Linux && ./UE4Editor
At this stage you should be able to have Unreal Engine up and running.
Downloading aria2 with sudo apt-get install aria2 will speed up the following commands.
1.Clone CARLA using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/carla-simulator/carla
2.You will need to download the latest assets to work with the current version of CARLA. We provide a script to automate this process. To use the script, run the following command in the CARLA root folder:
3.Set Unreal Engine environment variable: For CARLA to find the correct installation of Unreal Engine, we need to set the CARLA environment variable.
- Open ~/.bashrc or ./profile with the following code:
gedit ~/.bashrcorgedit ~/.profile - Add the following line to the bottom of the file:
export UE4_ROOT=~/UnrealEngine_4.26 - Save the file and reset the terminal.
This section outlines the commands to build CARLA. All commands should be run in the root CARLA folder.
The Python API client grants control over the simulation. Compilation of the Python API client is required the first time you build CARLA and again after you perform any updates. After the client is compiled, you will be able to run scripts to interact with the simulation.
1.The following command compiles the Python API client: make PythonAPI
2.The following command compiles and launches Unreal Engine. Run this command each time you want to launch the server or use the Unreal Engine editor: make launch
3.start the simulation: now you should be able to see unreal engine window with the following texture and you should press the play button to start the server:
Now the CARLA server is running and is waiting to be connected to MATLAB or Python through port 2000.
In this stage we want to have the designed custom map to be loaded in Unreal Engine. The neccessary files can be found in the folder MAP which is included .fbx and .xodr files among with the other neccessary files. Those files need to be coppied and pasted in Import folder in CARLA root directory
after coppying is done, a terminal in CARLA root directory should be opened and run the the following command make Import
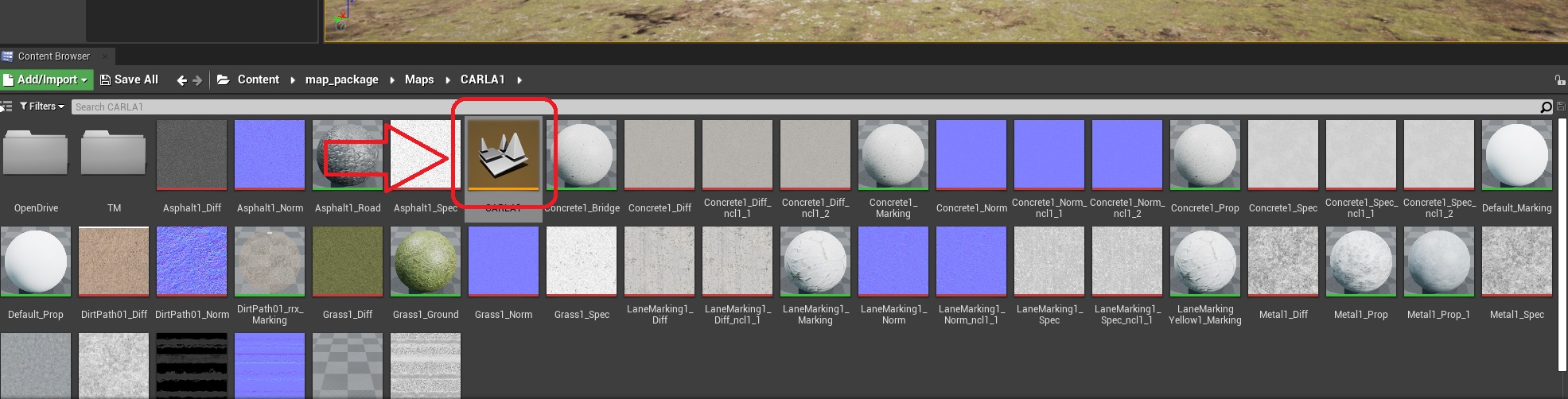
Now, the Map packages can be found in unreal engine in the following directory:
Content>map_package>Maps>CARLAXLBP>CARLAXLBP (which has a level tag and the icon is in yellow)
After setting up CARLA and Unreal engine, not it is the time to run the developed algorithem.
In generateTurnLeftScenario.m all the pathes and the desired pathes for cCar and uCar and all the other actors are defined as well as RSU-LiDAR attributes and its location. Waring time (TTC) and also safety range could be modified in that function also. For higher speed TTC and safety must be adopt carefully. In input section Timesteps and also Deceleration period are adjustable.
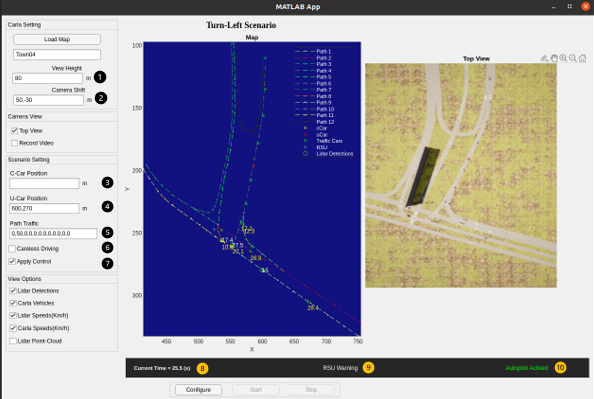
after setting all these parameteres which are defined as pre-defined properties you can double click on scenarioViewer.mlapp to run the desired scenarios. By clicking on scenarioViewer.mlapp the developed application will pop up and some parameteres can be changed and some explnation are neccessary which are listed below:
1.View height defines the height of the RGB camera for the top view
2.In this box user is able to shift the RGB camera for the top view.
3&4.User can either manually enter the coordinates of the map to set the position of the CCar, or leave it blank to have the CAT vehicle spawn randomly. (same is applicable for the 4th point for UCar)
-
Within this box, user can specify the number of vehicles to be spawned on their respective paths.
-
By checking careless driving check box, all the actors can be controlled via traffic manager (speed, collision detector, following distance and etc)
-
By checking apply control, CAT vehicle reads the proposed control algorithm (the reason for that was to evaluate CAT vehicle behaviour without control algorithm)
-
Current time shows the time of the simulation and it updates every 0.1s.
-
RSU warning shows the TTC upon issued warning.
-
when there is a warning received by the CAT vehicle autopilot activate changes to autopilot deactivate for 2 secs (this is just an indicator to see when the CAT vehicle is controlled by RSU)
When Careless driving is activated the user has the ability to control the following driving behaviour which can be found from line 143 to 168 in turnLeftScenario.m:
-
Set a minimum distance between stopped vehicles (for a single vehicle or for all vehicles). This will affect the minimum moving distance.
-
Set the desired speed as a percentage of the current speed limit (for a single vehicle or for all vehicles).
-
Reset traffic lights.
-
Enable/Disable collisions between a vehicle and a specific actor.
-
Make a vehicle ignore all other vehicles.
-
Make a vehicle ignore all walkers.
-
Make a vehicle ignore all traffic lights.
-
Force a lane change, ignoring possible collisions.
-
Enable/Disable lane changes for a vehicle.
-
Enable/Disable hybrid physics mode.
-
Change the radius in which physics is enabled.
Since in this project cCar and uCar are predefined and have different ID we can control both of them along with other actors.
For example if user wants to force the cCar to drive at 45km/h instead of 30km/h and uCar 15km/h instead of 30km/h following code should be changed in the mentiond matlab function.
obj.trafficManager.vehicle_percentage_speed_difference(obj.cCar, -5o); which means cCar should drive 50% more of the speed limit which will be 45 km/h
obj.trafficManager.vehicle_percentage_speed_difference(obj.uCar, 50); which means uCar should drive 50% of the speed limit which will be 15km/h
The framework has been designed for easy implementation in different locations, and as such, this section provides a detailed explanation for users on how to achieve this. For doing so we need to specify the following parametres in generateTurnLeftScenario.m:
- each path's coordinates (x,y)
- Center, which is the accident point
- The location of the RSU
- cCar and uCar path index
For achieveing the coordinates of each path, a vehicle can be spawned using manual_control.py and by doing that an approximation of the desired coordinates can be achieved as shown in th e picture.
e picture.
In order to obtain precise coordinates for lidar detection and path filtering, a Walker should be spawned and the following code can be used with a Python interface such as Jupyter Notebook, or any other interface that supports Python, using a trial and error approach.
import carla
import math
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2 # Connect the client and set up bp library and spawn points
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
world = client.get_world()
bp_lib = world.get_blueprint_library()
blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library()
bp1 = blueprint_library.filter("walker.*")[0]
#bp.set_attribute('color', '255,0,0') print(bp1)
spawn_point = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=554.4849,y=167.128, z=0.598),carla.Rotation(pitch=0.0, yaw=0.0, roll=0.000000)) vehicle = world.spawn_actor(bp1, spawn_point)
This process is time consuming since all the point should be achieved manually.
Once all the desired paths have been obtained, the LiDAR location must be chosen and placed at the desired point. This location is related to the accident point and may require trial and error to achieve the desired outcome. Additionally, the paths for both cCar and uCar should be selected to match the desired path.
For instance, to illustrate two different paths with different coordinates, let's consider the Xl BP entrance as an example.
path1.xRange=[634 599.259263852877 580.062802131787 574.87932675924 570.626554876634 570.038545025847 571.135913728272 ]; path1.yRange=[281 266.716758775826 258.787739854474 255.201958342648 248.764318606281 242.222252911202 233.992457812997 ]; path2.xRange=[754.407722890265 738.894749629363 714.875296281831 687.931711144475 666.295195806901 633.636304731318 604.252665977478 583.366144096083 574.517906691718 564.986154651883 551.504998869021 535.44146861407 530.542634952732 ]; path2.yRange=[322.536110677723 317.226565453074 308.779093708541 299.557252002573 292.151833662932 280.973843716304 272.275602592047 265.353338159967 261.871982606853 257.703768987282 251.73089830659 247.327086697693 243.650388205699 ];