-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 231
Create App Control Policy
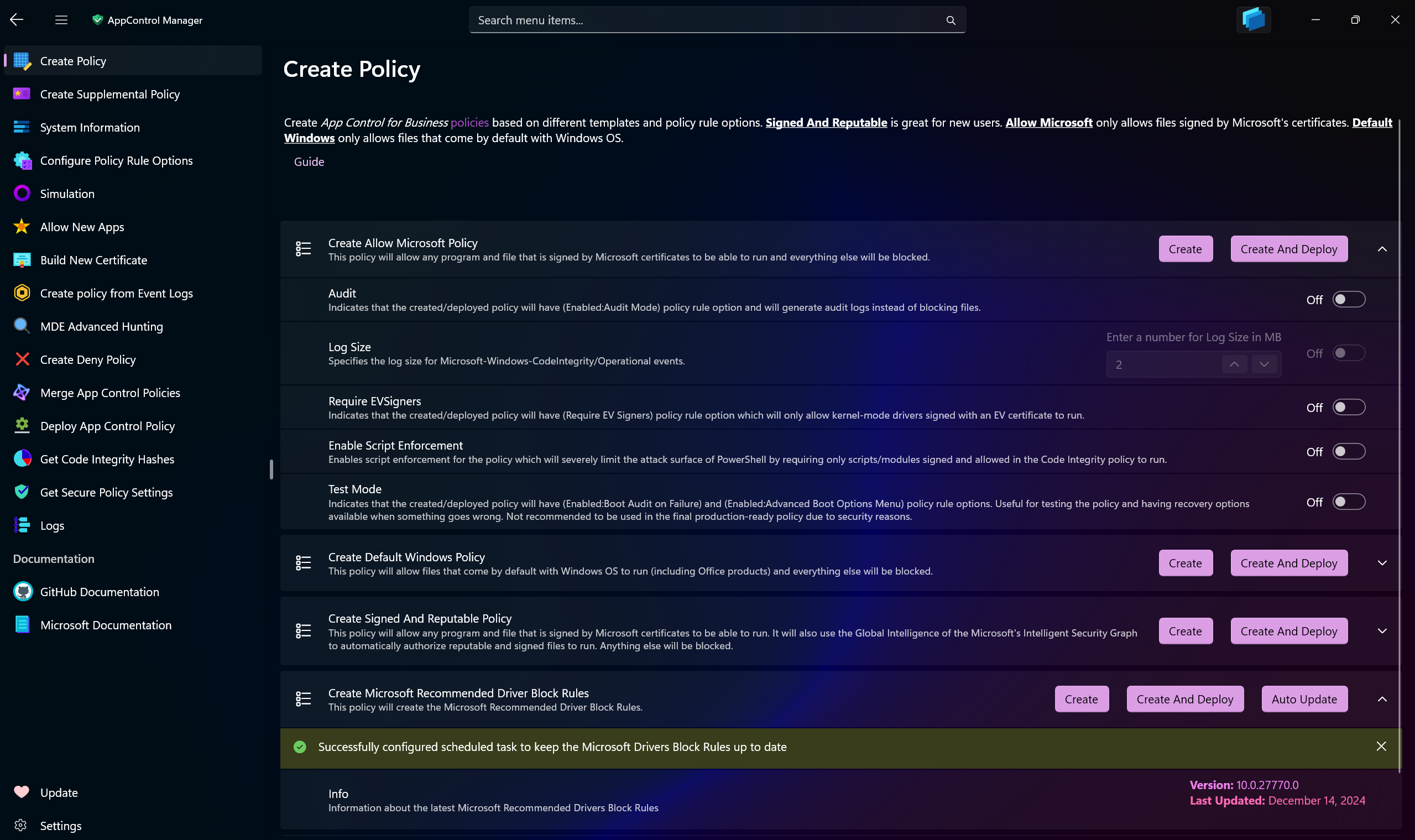
Use AppControl Manager to create new App Control policies based on the default templates.
-
Allow Microsoft: Only allows files signed by Microsoft certificates to run on the system.
-
Default Windows: Only allows files that come by default with Windows OS to run on the system.
-
Signed And Reputable: Allows files signed by Microsoft certificates to run, it also utilizes the Intelligent Security Graph to allow files that are reputable and safe.
-
Microsoft Recommended Block Rules: It will download the latest Microsoft Recommended (User-Mode) block rules from the official source and create an App Control policy.
-
Microsoft Recommended Driver Block Rules: It will download the latest Microsoft Recommended (Kernel-Mode) block rules from the official source and create an App Control policy.
- Auto update: It will create a scheduled task on the system that will check every week for the latest Microsoft Recommended block rules and update the policy automatically. Please refer to this page for more info.
-
Strict Kernel-mode policy: It's a special kind of policy that will only enforce Kernel-mode files without blocking user-mode files. Please refer to this article for more information.
Deploying any of them is optional. You can create the policies and then deploying them on remote systems using Intune or other methods.
There are different settings and options you can use to fine tune the policy according to your requirements.
-
Audit: When a policy has Audit mode turned on for it, it will only log the events and not block any files from running.
-
Log Size: You can configure the max capacity of the
Code Integrity/Operationallog size. It is recommended to increase it from the default1MBcapacity if you want to begin auditing for App Control events. When the capacity is reached, the log will overwrite the oldest events. -
Require EVSigners: When this setting is enabled, the policy will only allow files signed by Extended Validation (EV) certificates to run on the system.
-
Enable Script Enforcement: When this setting is enabled, the policy will only allow PowerShell scripts or modules that are signed and their signing certificates are allowed in an App Control policy to run. This greatly reduces the attack surface from the Windows script hosts.
-
Test Mode: Boot Options Menu, such as Safe mode, is disabled for all App Control policies by default. Using Test Mode will allow access to it. It will also automatically enable the
Auditmode for the policy in case of a failure in a driver that is critical to system boot. It's only recommended to use this setting in a test environment and not in production due to security reasons.

To combat the threat of more sophisticated malware, a preemptive measure is taken by creating and deploying an App Control policy on the system. This policy blocks the execution of executables and other potentially harmful file types in the Downloads folder.
This policy defends the system from malware that can launch itself automatically after being downloaded from the Internet and has the potential to protect against zero-click exploits. The user must ensure the file's safety and explicitly transfer it to a different folder before running it.
The App Control policy employs a wildcard pattern to prevent any file from running in the Downloads folder. Additionally, it verifies that the system downloads folder in the user directory matches the downloads folder in the Edge browser's settings. If there is a discrepancy, a warning message is displayed on the console.

Creates a custom App Control policy that blocks the execution of the following executables:
- wscript.exe
- mshta.exe
- cscript.exe
They are insecure, unsandboxed script hosts that pose a security risk.
- Create AppControl Policy
- Create Supplemental Policy
- System Information
- Configure Policy Rule Options
- Policy Editor
- Simulation
- Allow New Apps
- Build New Certificate
- Create Policy From Event Logs
- Create Policy From MDE Advanced Hunting
- Create Deny Policy
- Merge App Control Policies
- Deploy App Control Policy
- Get Code Integrity Hashes
- Get Secure Policy Settings
- Update
- Sidebar
- Validate Policies
- View File Certificates
- Microsoft Graph
- Protect
- Microsoft Security Baselines
- Microsoft Security Baselines Overrides
- Microsoft 365 Apps Security Baseline
- Microsoft Defender
- Attack Surface Reduction
- Bitlocker
- Device Guard
- TLS Security
- Lock Screen
- User Account Control
- Windows Firewall
- Optional Windows Features
- Windows Networking
- Miscellaneous Configurations
- Windows Update
- Edge Browser
- Certificate Checking
- Country IP Blocking
- Non Admin Measures
- Group Policy Editor
- Manage Installed Apps
- File Reputation
- Audit Policies
- Introduction
- How To Generate Audit Logs via App Control Policies
- How To Create an App Control Supplemental Policy
- The Strength of Signed App Control Policies
- How To Upload App Control Policies To Intune Using AppControl Manager
- How To Create and Maintain Strict Kernel‐Mode App Control Policy
- How to Create an App Control Deny Policy
- App Control Notes
- How to use Windows Server to Create App Control Code Signing Certificate
- Fast and Automatic Microsoft Recommended Driver Block Rules updates
- App Control policy for BYOVD Kernel mode only protection
- EKUs in App Control for Business Policies
- App Control Rule Levels Comparison and Guide
- Script Enforcement and PowerShell Constrained Language Mode in App Control Policies
- How to Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Hunting With App Control
- App Control Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- System Integrity Policy Transformations | XML to CIP and Back
- Create Bootable USB flash drive with no 3rd party tools
- Event Viewer
- Group Policy
- How to compact your OS and free up extra space
- Hyper V
- Git GitHub Desktop and Mandatory ASLR
- Signed and Verified commits with GitHub desktop
- About TLS, DNS, Encryption and OPSEC concepts
- Things to do when clean installing Windows
- Comparison of security benchmarks
- BitLocker, TPM and Pluton | What Are They and How Do They Work
- How to Detect Changes in User and Local Machine Certificate Stores in Real Time Using PowerShell
- Cloning Personal and Enterprise Repositories Using GitHub Desktop
- Only a Small Portion of The Windows OS Security Apparatus
- Rethinking Trust: Advanced Security Measures for High‐Stakes Systems
- Clean Source principle, Azure and Privileged Access Workstations
- How to Securely Connect to Azure VMs and Use RDP
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 2
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 3
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 4
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 5
- How To Access All Stream Outputs From Thread Jobs In PowerShell In Real Time
- PowerShell Best Practices To Follow When Coding
- How To Asynchronously Access All Stream Outputs From Background Jobs In PowerShell
- Powershell Dynamic Parameters and How to Add Them to the Get‐Help Syntax
- RunSpaces In PowerShell
- How To Use Reflection And Prevent Using Internal & Private C# Methods in PowerShell
