-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 114
Developer's Guide
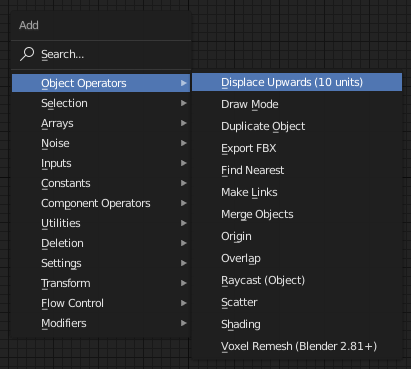
Let's create a node that operates on "Object" mode and displaces the selected (active) object in the viewport by +10 units in Z axis (upwards).
-
Navigate to <Sorcar dir>/nodes/<category>
.../Sorcar/nodes/object_operators in this case.

-
Create a new file Sc<ShortName>.py
Let us name the file "ScDisplaceUp.py". This name must be unique. The display name (called label) can be changed later in the code, for example "Displace Upwards (10 units)".
- Open the created file and import Blender's python package
import bpy - Import Blender's node base class and Sorcar's base classes
from bpy.types import Node
from .._base.node_base import ScNode
from .._base.node_<category> import Sc<Category>NodeSorcar's base classes include methods to execute the node and manage input & output socket values. They also create a suitable environment (correct object selection, mode, etc.) before executing. For more information on base categories, look at .../Sorcar/nodes/_base/ directory.
- Create a class (having the same name as the file) which inherits from Node and Sc<Category>Node
class Sc<ShortName>(Node, Sc<Category>Node): - Set attributes bl_idname and bl_label
bl_idname = "Sc<ShortName>"
bl_label = "<Small Description>"
import bpy
from bpy.types import Node
from .._base.node_base import ScNode
from .._base.node_operator import ScObjectOperatorNode
class ScDisplaceUp(Node, ScObjectOperatorNode):
bl_idname = "ScDisplaceUp"
bl_label = "Displace Upwards (10 units)"
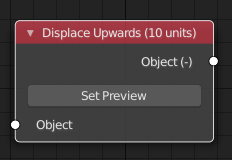
Let us add two input sockets of different types and one output socket. For more information on available socket types in sorcar, see .../Sorcar/sockets/ directory.
- Override function init(self)
def init(self): - Call init() method of the parent class before implementing custom sockets
super().init()
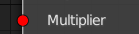
Let's add a boolean input socket with name "Multiplier" which we will use later to check if the displacement should be multiplied by a factor.
-
Add a new input socket of a specific type with a unique display name
self.inputs.new("ScNodeSocket<Type>", "<Display Name>")https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.NodeInputs.html#bpy.types.NodeInputs.new
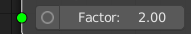
Let's add a float (number) input socket with name "Factor" which we will use later to multiply the default displacement value (i.e. 10).
-
Import Blender UI property
from bpy.props import <Type>Property -
Create a property inside the class with prefix in_
in_<name>: <Type>Property(..., ..., update=ScNode.update_value) -
Add a new input socket referencing the created property
self.inputs.new("ScNodeSocket<Type>", "<Display Name>").init("in_<name>")By default, the property remains hidden in the node. It can be accessed by the N-Panel in the Node Editor. To set the input socket to visible by default, override the argument of init() method:
self.inputs.new("ScNodeSocket<Type>", "<Display Name>").init("in_<name>", True)
Let's add a float (number) output socket with name "Factor" which will store the actual value of displacement (10 x Factor).
-
Add a new output socket of a specific type with a unique display name (input & output sockets can have the same name)
self.outputs.new("ScNodeSocket<Type>", "<Display Name>")https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.NodeOutputs.html#bpy.types.NodeOutputs.new

in_factor: FloatProperty(default=2.0, min=0.0, update=ScNode.update_value)
def init(self, context):
super().init(context)
self.inputs.new("ScNodeSocketBool", "Multiplier")
self.inputs.new("ScNodeSocketNumber", "Factor").init("in_factor", True)
self.outputs.new("ScNodeSocketNumber", "Factor")
Once the node structure is implemented, we need to make sure that each input value is correct (e.g. Enum) or in the required range (e.g. Number).
- Override function error_conditions(self)
def error_conditions(self): - Return the boolean value ensuring that error_condition() method of the parent class is among the conditions checked
return (super().error_condition() or <condition> or <condition>)
def error_condition(self):
return (
super().error_condition()
or (self.inputs["Factor"].default_value < 0.0)
)
Sorcar's base category classes automatically create the required environment for the node to execute in. However we can further change or modify the scene (say delete all objects or recenter the selected object) as per the requirements.
- Override function pre_execute(self)
def pre_execute(self): - Optionally, call pre_execute() method of the parent class (order of the call matters)
super().pre_execute()
Once the environment is set, we can modify the scene or object in the intended way. We can use the input socket values to drive the function arguments.
- Override method functionality(self)
def functionality(self): - Access the input values
self.inputs["<Display Name>"].default_value - Write the functionality of the node using input values as required
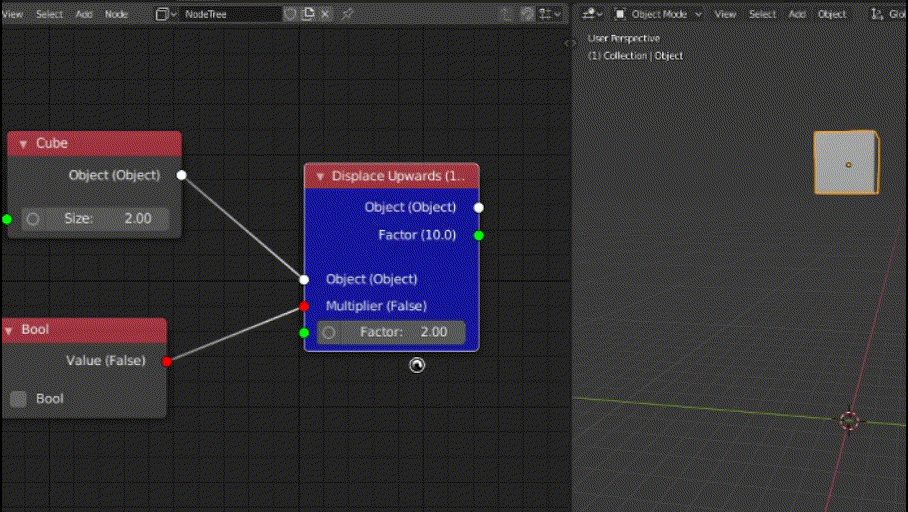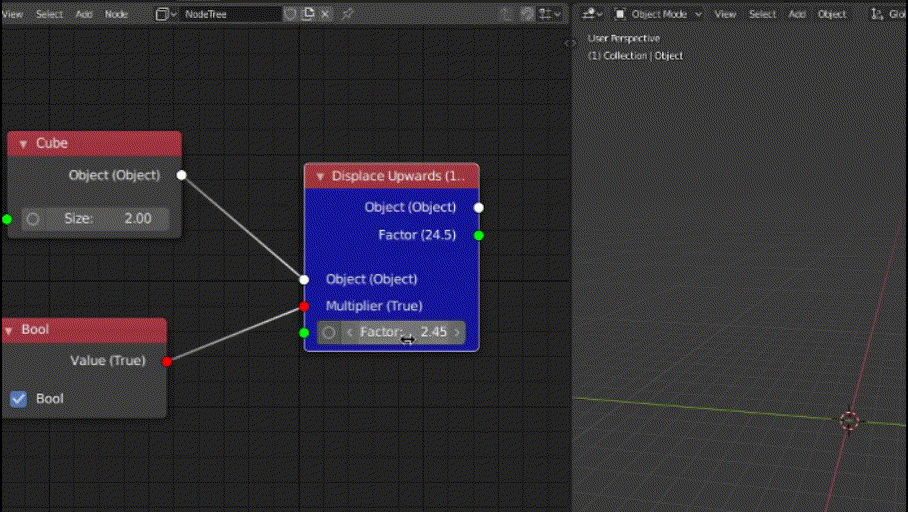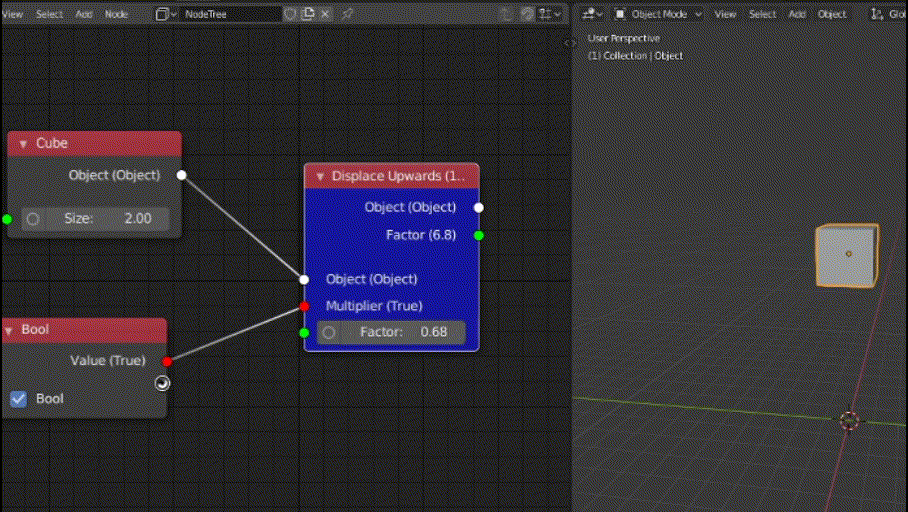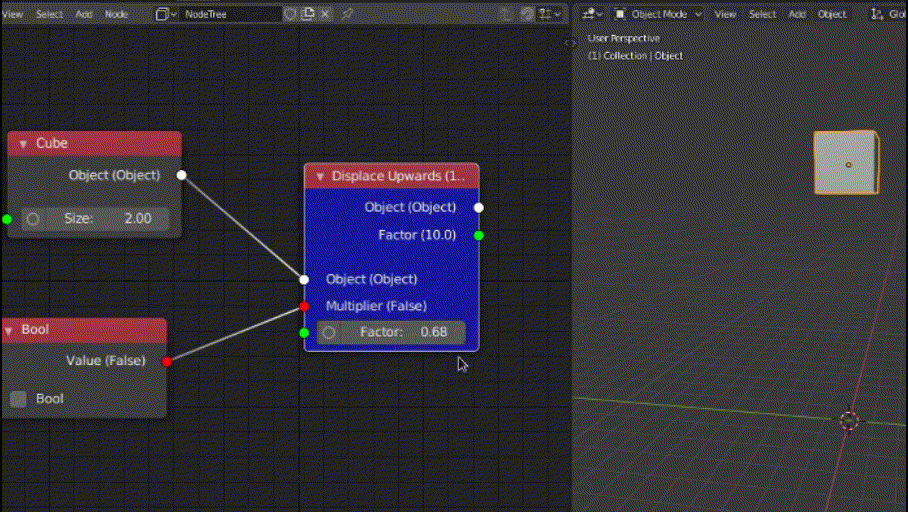
In this function, we will access the "Multiplier" boolean input value and check if we need to multiply the default value (i.e 10) by the "Factor" input value. If not, then we will set the 3rd index (Z) of "location" attribute of the input object (socket provided by base class).
def functionality(self):
if (self.inputs["Multiplier"].default_value):
self.inputs["Object"].default_value.location[2] += 10 * self.inputs["Factor"].default_value
else:
self.inputs["Object"].default_value.location[2] += 10
After the main functionality of node gets executed, we need to set the custom output node values manually. Sockets provided by the base category classes are not required to be set, but can be overridden if required.
- Override method post_execute(self)
def post_execute(self): - Get the results from parent class
out = super().post_execute() - Add values for corresponding output sockets in the obtained dictionary
out["<Display Name>"] = <value>
out["<Display Name>"] = <value>
out["<Display Name>"] = <value> - Return the dictionary
return out
Since we only have one custom output socket, we will access the "Multiplier" boolean input value again, check if we need to multiply the default value (i.e 10) by the "Factor" input value and set it to the output socket for further use.
def post_execute(self):
out = super().post_execute()
if (self.inputs["Multiplier"].default_value):
out["Factor"] = 10 * self.inputs["Factor"].default_value
else:
out["Factor"] = 10
return out
- Variables declared outside any function (in the class body) without using Blender's property types are immutable.
- Certain data-types use common sockets to transfer information, such as:
- Int, Float, Angle --> Number socket
- String, Enum --> String socket
- Array (of size 3), Vector --> Vector socket
- Since the whole node network is re-evaluated on any value change, it is crucial to optimise as much as possible to reduce processing time (higher FPS)
- Use bpy.ops inbuilt functions wherever possible rather than writing your custom implementation.
- These functions are provided for the convenience of the developer. You can create your own functions as well. Make sure that the flow of execution doesn't get affected:
...<-[output<-node<-input]<-[output<-node<-input]<-[output<-node<-input]<-...
Component Operators
- Add Edge/Face
- Average Normal
- Beauty Fill
- Bevel
- Bisect
- Bridge Edge Loops
- Connect Vertices
- Convex Hull
- Decimate
- Duplicate Component
- Extrude
- Extrude Edges (Individually)
- Extrude Faces (Individually)
- Extrude Region
- Extrude Vertices (Individually)
- Fill Edge Loop
- Fill Grid
- Fill Holes (By Sides)
- Flatten
- Flip Normals
- Inset
- Intersect
- Intersect Boolean
- Loop Cut
- Make Normals Consistent
- Material
- Merge
- Merge Normals
- Offset Edge Loops
- Point Normals
- Poke
- Quadrangulate
- Remove Doubles
- Rip
- Rip Edge
- Rotate Edge
- Screw
- Separate
- Solidify
- Spin
- Split
- Subdivide
- Subdivide Edge Ring
- Symmetrize
- Snap To Symmetry
- Triangulate
- Unsubdivide
- UV Project
- UV Smart Project
- UV Unwrap
- Vertex Group
- Wireframe
Modifiers
- Array Modifier
- Bevel Modifier
- Boolean Modifier
- Build Modifier
- Cast Modifier
- Corrective Smoothness Modifier
- Curve Modifier
- Decimate Modifier
- Displace Modifier
- Edge Split Modifier
- Hook Modifier
- Laplacian Smooth Modifier
- Mirror Modifier
- Remesh Modifier
- Screw Modifier
- Simple Deform Modifier
- Skin Modifier
- Smooth Modifier
- Solidify Modifier
- Subdivision Surface Modifier
- Triangulate Modifier
- Wave Modifier
- Wireframe Modifier
Selection
- Select All
- Select Alternate faces
- Select Axis
- Select By Index
- Select By location
- Select By Material
- Select By Normal
- Select By Vertex Group
- Select Face By Sides
- Select Interior Faces
- Select Less
- Select Linked
- Select Linked Faces By Angle
- Select Linked Pick
- Select Loop
- Select Loop Region
- Select Loose
- Select Manually
- Select Mirror
- Select More
- Select Multi-Loop
- Select Next Item
- Select Non-manifold
- Select Nth (Checker Deselect)
- Select Previous Item
- Select Random
- Select Region Boundary
- Select Sharp Edges
- Select Shortest Path
- Select Shortest Path Pick
- Select Similar
- Select Similar Region
- Select Ungrouped